Principle:
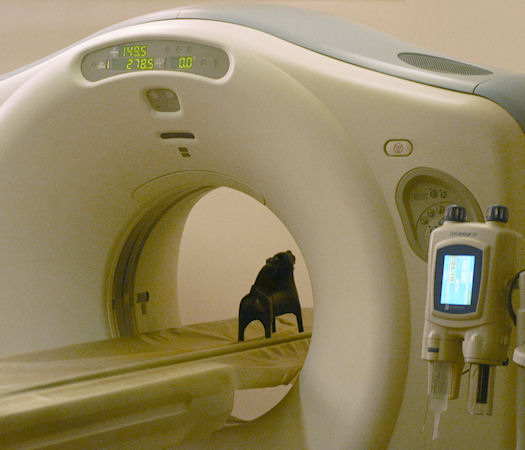
X-rays pass through a presented object, losing their intensity depending on resistance encountered.
An x-ray tube turns around the object and produces either closely or widely linked (overlapping) slices.
The reconstituted image enables successive slices of the object to be examined in three dimensions.
Applications:
– Metallic, wooden, plastic objects … but not glass.
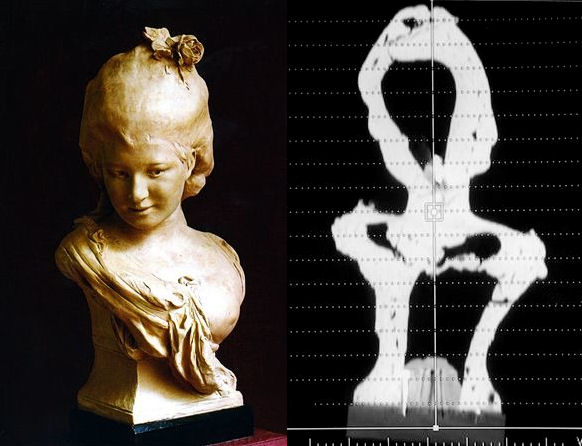
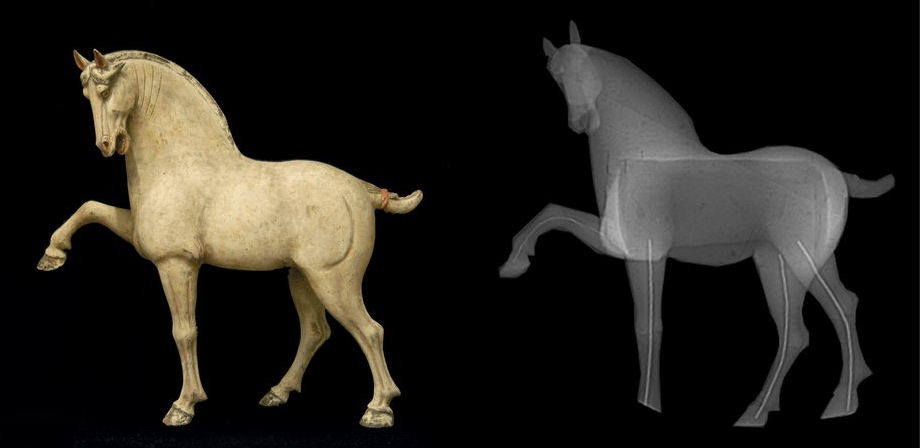
Very precise internal observations. Reconstruction of lost areas or those to be removed.
Non-destructive interior view that permits, among other things, discovery of items added and assembled work that is not visible from the exterior.